Cloud Powered Solutions carry a lot of inherent benefits for any deploying organization. Today’s business environment is highly competitive and corporate entities remain on the lookout for ways to drive costs down and improve organization efficiency.
Also Read:
- How Cloud Computing Helps You Attain Business Goals?
- How a Cloud Powered Digital Workspace Benefits an Organization?
- How Cloud Computing Can Bring Efficiency and Ease in Healthcare?
Without doubt, a well-orchestrated Cloud Computing Solution is bound to bring about efficiency and saving to an organization. However, selecting the appropriate cloud deployment model is a very crucial decision, as entities cannot afford to constantly switch between cloud architectures.
In this post, we will first outline the difference between a public and private cloud. Then, we will highlight certain factors that should facilitate you in choosing the suitable deployment model for your entity. Remember it’s not about good or bad, rather what’s most appropriate in a given scenario.
Also Read: Public and Private Cloud Infrastructures
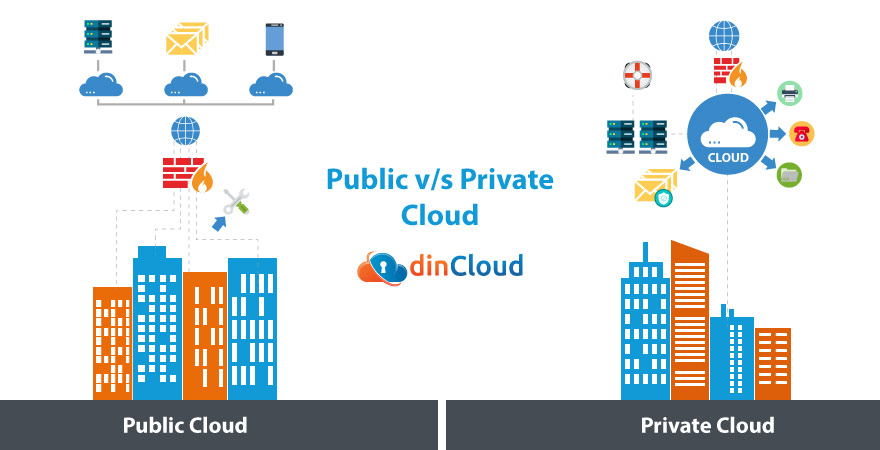
Public Cloud
This is the more common deployment model when it comes to the cloud. In a public cloud, a large Cloud Service Provider invests heavily in vast data centers with immense storage and processing muscle. Virtualized services such as storage, computing and database management are then offered by these CSPs.

In most cases, the potential users of the public cloud are organizations that are not dealing with highly sensitive data or lack the resources of setting up an on premise data center. To manage its huge capital expenditures, a CSP will offer its virtualized services to a large number of organizations of different size and industries.
A public cloud will utilize our every day internet which will act as a bridge between the CSP and its end user. In the public cloud, all the hardware is procured, maintained and configured by the CSP. In exchange for using its hardware, the CSP will charge the end user a pre defined fee.
This fee is generally variable and depends on the type and scale of resources you are using from the CSP. This results in cost saving for the cloud tenant as no heavy capital expenditures are required to connect to the public cloud. Even for login devices, you can easily manage with low spec hardware with.
Also Read: Top 10 Emerging Cloud Computing Trends for 2020
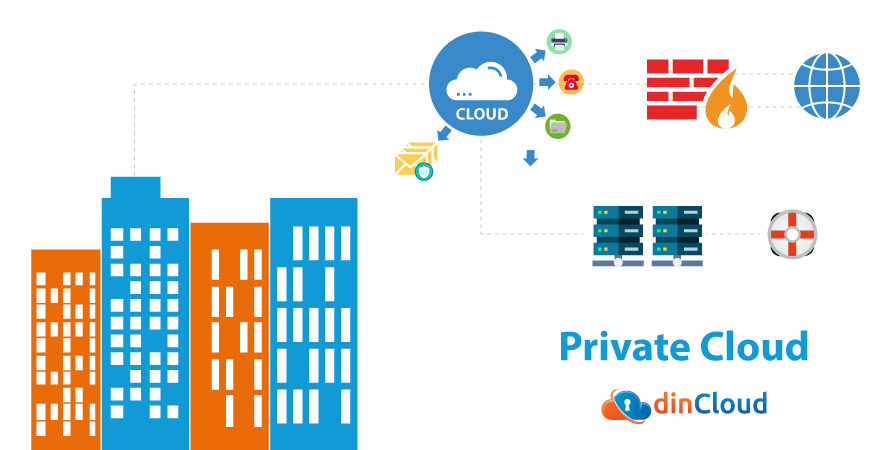
Private Cloud
As the name suggests, this is an exclusive virtualization solution in which a central data center is set up generally within the organization’s premise. Virtual Machines (VM) also called Virtual Desktops are then created over this converged hardware and served across the organization.
In some rare cases, a private cloud may be set up between a select few organizations. So far as end user experience is concerned, there is hardly a major difference between the two virtualization architectures. However, setting up a data center on premise is a very costly affair.
The higher costs do not just stop at setting up of the data center, as the deploying organization is solely responsible for maintaining this hardware in optimal working condition. The upsides are that the private cloud is generally more efficient that the public cloud and the deploying entity enjoys more control over its data.
Also Read: 11 Cloud Computing Predictions for the Year 2020
A private cloud is mostly served through an intranet for enhanced security. In some rare cases, a private cloud may also use the internet but in that case, a robust cyber security mechanism has to be put in place, which further adds to the costs and technical complexities.
Now that we have outlined how the public and private clouds work, let’s briefly discuss their respective application scenarios so that you can choose the most suitable deployment model for your organization.
When to Use Public Cloud
- Cost management is a major consideration
- Internet bandwidth and connectivity is excellent
- Data or information is not of a very sensitive nature
- Your scalability needs are constantly fluctuating due to seasonal trends
- The computing needs are not very complex in nature
- In house IT expertise is a limiting factor
Private Cloud Usage Cases
- Suited for medium to large sized organizations
- Lower costs are not a key consideration
- Internet bandwidth and performance is slow or unreliable
- Organization handles data of sensitive or personal nature
- The IT resources can be planned with a fair degree of predictability
- Highly customized and complex computing or processing needs
- When higher latency cannot be tolerated by the organization
- Level of in-house IT and virtualization expertise amply exists
Also Read: Cloud Computing and Strategic Business Advantages 2020
Conclusion
In this post, we have not only highlighted the differences between the public and private cloud, we have also outlined the suitable usage scenarios for each cloud computing architecture. Before going for any of these solutions, an organization must carefully outline its needs and limiting factors to get the best results.


