In the pursuit of flexibility, scalability and reducing costs, businesses are shifting to Cloud Solutions more than ever. The decision to deploy cloud based solutions is without prejudice to the size of an entity and we even see industry leaders rapidly adopting the cloud.

The only alarming trend is that news about security and data breaches over the cloud are constantly gracing the tech related top stories. The stakes get even higher when the data breach pertains to either an industry giant or where data related to thousands and millions of individuals is involved.
Also Read: Equifax Massive Data Breach | Equifax To Pay Upto $700 Million For Breach Settlement
In cases of data breach where the affected organization is large, the common scapegoat of resource constraints cannot be cited. Secondly, no sane person can opt in favor of a cloud solution at the cost of data security. Any decent cloud based solution is presumed to be flexible, efficient and most importantly secure.
Also Read: 8 Reasons: Why Cloud Computing For Small Business?
Perhaps this presumption about a failsafe security of any cloud network is also a major weak link. Based on this approach, organizations deploying a cloud solution tend to become complacent and the reckless actions of a handful of employees can put the entire network of an organization at risk.
Shared Responsibility Model
The most realistic approach to cloud security is the well rounded shared responsibility model. It does not shift the entire burden of securing the cloud either on the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) or the tenant entity. Both have their respective roles in securing the cloud from all threats, be it internal and external.
Responsibility of Cloud Service Provider
In an outsourced cloud solution, the ultimate repository of the data is a CSP’s data center. It is logical that once data is safely parked at the data center, securing it should be the headache of CSP. User authentication protocols are the second most important pillar of cloud security at the CSP level.
All the user authentication protocols are adopted by the cloud deploying entity that will choose from a host of available options. The two most important considerations will be administrative feasibility and affordability. Medium to large sized organizations can afford the luxury of employing multi-factor authentication protocols.
Tenant Organization’s Responsibility
Even the most extensive and latest cloud security measures will go in vain if a deploying organization shows any lapse in implementing those measures and controls. The two most vital components of cloud security at the entity level are securing the unique login credentials and the devices used to access the cloud network.
Also Read: Protecting Your Business from Cyber Attacks
If a user’s login credentials fall in the wrong hands, an intruder can easily impersonate a legitimate user and wreak havoc over the cloud. This concern becomes even more serious if the stolen credentials pertain to a user who grants access related authorization to other cloud users.
The other critical aspect of organization level security is to avoid unauthorized use of a device that is used to access the cloud network. Not only will it create problems for the careless employee, but will also make it even more difficult to locate the perpetrator.
Major Cloud Security Breaches of 2019
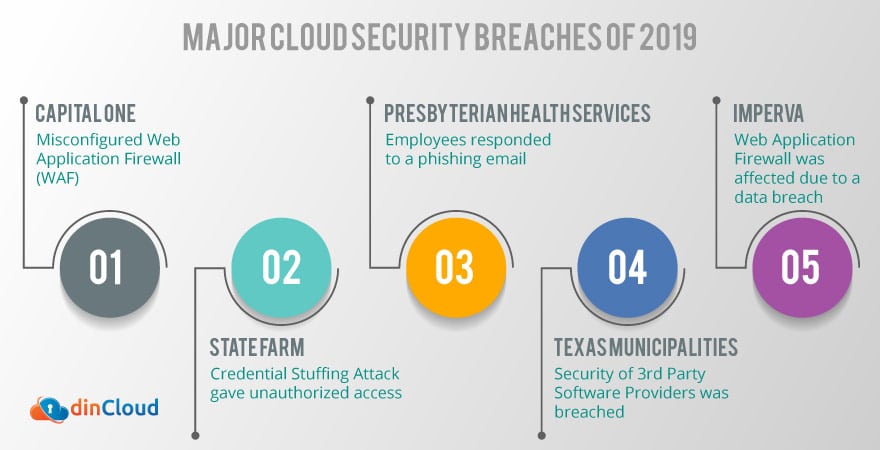
The year 2019 has been marred with several reported incidents of cloud security breaches. Rest assured that the actual incidents, both identified or otherwise, are more than the reported numbers. Let’s cover some of the major reported cases and draw a few insightful conclusions for the future.
Capital One
It is the 10th largest bank in America on the basis of assets. It uses the revered Amazon Web Services (AWS) as its cloud solution. Here is the chain of fateful events leading to the breach.
- A Web Application Firewall (WAF) was misconfigured.
- Its function is to stop any unapproved access.
- The attacker generated an access token using the misconfigured WAF.
- Access token was then used to fetch data from AWS storage.
- 700 folders and data packets containing customer info were copied to an external location.
The attacker was privy to specialized AWS commands which were used once access was granted to the network. Secondly, the perpetrator did not raise any typical red flags of a cyber attack. Even the transfer of data outside the network of Capital One was performed in line with the routine network traffic load.
State Farm
It is an American group of insurance and financial services companies. State Farm’s data breach was shockingly caused by a credential stuffing attack. In this attack, the stolen passwords from a previous, unrelated data breach are used by an attacker to attempt login into other random services.
State Farm reiterated its customers that this unauthorized access to their accounts did not result in any fraud or personally identifiable information (PII) leak. Notwithstanding these claims, it is highly likely that if the entire user accounts were successfully accessed, some information breach was certain.
Presbyterian Health Services
It is a health care provider that operates across New Mexico. Its data was compromised when several employees responded to a phishing email. As a result, hackers were able to gain access to highly confidential health information of nearly quarter million citizens.
Also Read: Petya Ransomware Cyberattack and How to Safeguard Against Future Attacks
Texas Local Governments
A whopping 22 municipalities of Texas became the victim of a ransom ware attack. The attacker gained access to critical state information by infiltrating the security of third party software providers. The state institutions in Texas heavily rely on such parties to execute their tasks in a cost effective manner.
Once the attacker infiltrated the data, it was then crypto locked and a ransom of $2.5 Million was demanded by the attacker for unlocking the data. The locked out data included state statistics, credit card payments and utility disconnections related to thousands of citizens.
Imperva
The mind boggling fact about Imperva is that it is itself a well reputed company that specializes in cyber security products. Its data breach affected the users of a critical product called Web Application Firewall (WAF). Its function is to control access to the cloud network where it is deployed.
As WAF controls the rules and protocols for granting cloud access, its breach can render the entire cloud network defenseless against any intrusion. The compromised data included emails addresses, scrambled passwords, SSL Certificates and API Keys.
Key Takeaways from 2019 Data Breaches
A total of 5 major data breaches of 2019 have been highlighted in this post. An alarming factor about these attacks is that each attack exploited a different vulnerability of the cloud network. The target organizations belong to different industries and are of different sizes, from small to large.
This also defeats the argument that as large organizations spend more on cyber security, they are bound to be immune from cyber threats. Cyber criminals did not even spare the very company that provides cloud security solutions to countless other organizations.
For getting a bird’s eye view of how each organization’s cyber security was breached, let’s study the table.
[table id=11 /]
How to Protect Your Entity from Attacks – The Way Forward
The wide array of affected organizations and cyber weapons used sufficiently underscore the gravity of cyber threats. Below are a few steps that will be critical to securing the cloud network of organizations of any size and belonging to any industry.
Also Read: 12 Security Questions to Ask From Your Cloud Solution Provider
Perception Shift
The first step in the journey towards cyber security is a shift in the underlying perception about cyber threats and security. In today’s cloud driven ecosystem, no organization of any size is aloof from the eyes of cyber criminals. This argument also extends to the industry spectrum, as no sector can be declared fully irrelevant for cyber thieves.
Secondly, this shift in cyber threat perception must travel from the top most tier of the company’s management. This will then gradually trickle down right to the end user of the cloud network. Once top management is pursuing cyber security initiatives, progress will be robust and resource related bottlenecks will not arise.
In today’s cyber space, it is no more a relevant question that whether a company’s cloud network will be attacked or not. Rather it should only be taken as a matter of when, where and how. Once this overall perception shift takes shape, any company will start making rapid progress towards the ultimate goal of cyber security.
The last critical component of changing the perceptions is how organizations that are affected by a cyber attack publicly handle the situation. A common tendency is to downplay and suppress the true gravity of the situation. Although it can pay short lived dividends but the long term effects can be devastating.
Once a data breach has been effected, the company involved must come clean about the situation and take all the key stakeholders into confidence. This will go a long way in preserving the overall image of the company in the context of corporate social responsibility.
Timely Detection and Response to Threats
Even the most well orchestrated cyber attacks can be repelled or mitigated if they can be detected in a timely fashion. Instead of reacting to a cyber threat or attack, companies will have to adopt a proactive approach to securing their cloud networks.
Threat response is a two pronged strategy. Firstly, an affected entity will immediately plug the loopholes that could or were exploited in a cyber attack. Let’s revert to the example of Capital One in which the entire network was exposed merely because of a misconfigured Web Application Firewall (WAF).
The second most critical aspect is threat response. This response will mainly focus on mitigating the damage of an already exploited weakness in the company’s cloud security apparatus. This phase should also involve questions like which other areas of the network may have possibly been left vulnerable by this breach.
A company’s threat response strategy should also involve the respective law enforcement agencies that specialize in cyber crime. An organization may have the world’s best cyber security analysts but many enforcement organizations enjoy unparalleled special permissions and powers that can be very fruitful in the event of a cyber attack.
Network Traffic Monitoring
An in depth, analytical and constant monitoring of network traffic can be an excellent barometer for timely detection of a cyber threat or attack in progress. The most lethal weapon of any cyber criminal is to blend in the normal traffic across the network to the best extent possible.
However, with a constant and critical approach to network traffic monitoring, even the most stealthy miscreant can be identified. A close eye on network traffic also serves as a means of an internal control mechanism. It can also identify any security loophole in the way data is routinely transmitted over the cloud network.
Access Management
Strong access management protocols go a long way in securing the cloud network as they serve as a gateway. Once a user, legitimate or otherwise, gets past the authentication phase, the whole cloud network may essentially be accessible. The access to the cloud network must be based on multiple and user centric attributes.
Some examples of a multi factor authentication protocol can be fingerprint, one time password, random number generator or any other attribute that is either dynamic or specific to each individual user. Such controls will keep the cloud network secure even if a user’s device is stolen or compromised.
These access management controls will also be instrumental in positively identifying any internal sabotage attempt by one of the company’s rogue employees. Close network traffic monitoring, coupled with strong access controls will make the organization’s cloud virtually impervious to internal threats.
CSP and Tenant Coordination
Although this area is relatively ignored, there needs to be a regular and close coordination between the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) and the organization’s network security analysts. This will highlight any vulnerability or abnormal network activity in a timely manner.
Employee Awareness and Training
Organizations need to invest time and resources in sensitizing and training their employees about cyber security. Each employee is a critical piece of the puzzle in securing the overall cloud network. Recall the example of Presbyterian Health Services whose multiple employees responded to phishing emails.
In hindsight, this was a simple and idiotic lapse on the part of a few employees but they must be given the margin of doubt that the company may never have sensitized them about receiving and reporting suspicious emails. They simply responded to those mails in the normal course of their day to day tasks.
This also extends to inculcating a sense of responsibility in each employee that the device used to access the cloud must not fall in the hands of an unintended user. Employees must also keep their login credentials strictly private, even among themselves.
Third Party Services
Companies that engage third party software or productivity applications must be very cautious about selecting the vendor. As this is generally done due to human or financial constraints, most companies end up deploying substandard and vulnerable solutions.
Whenever 3rd party solutions are deployed in conjunction with a company’s cloud network, they must prequalify certain minimum cyber security standards for the respective industry or sector. Mere low cost should never be the defining criterion for such solutions as they render the whole network highly vulnerable.
Conclusion
It this detailed post, we have covered a host of cyber attacks in the year 2019. We also highlighted the weakness exploited in each attack and have also given a detailed road map for securing your cloud network. Securing the cloud is not a destination, rather a journey.
A journey that demands vision, understanding, ownership, persistence and resources to realize the ultimate goal of securing your cloud network. The benefits of cloud computing solutions are so compelling that instead of shying away from them, why not fully tap the potential by making your cloud network secure.


